Customer Publication
BRAFV600E induces reversible mitotic arrest in human melanocytes via microRNA-mediated suppression of AURKB
Journal: eLife (2021)
Institution: University of California
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: Benign human melanocytic nevi, 501Mel, HCIMel019 (human melanoma line)
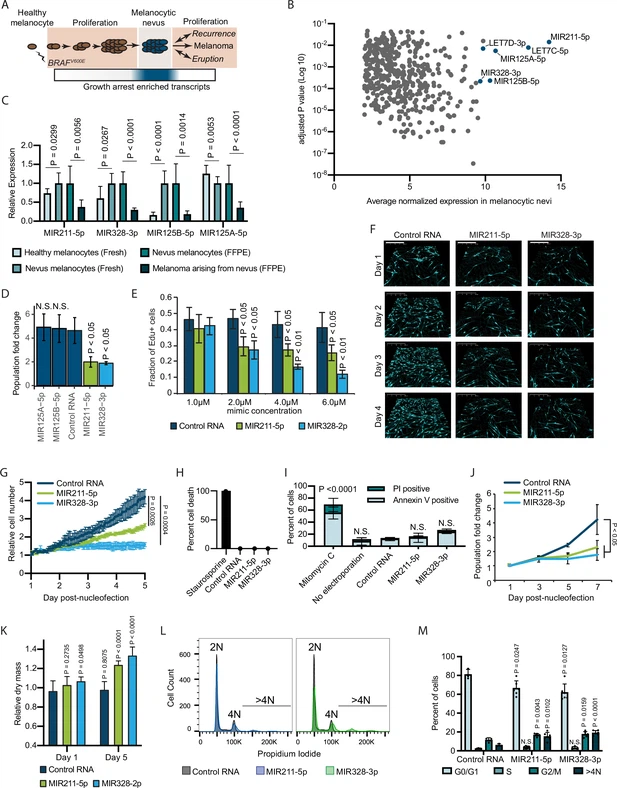
Summary: Benign melanocytic nevi frequently emerge when an acquired BRAFV600E mutation triggers unchecked proliferation and subsequent arrest in melanocytes. Recent observations have challenged the role of oncogene-induced senescence in melanocytic nevus formation, necessitating investigations into alternative mechanisms for the establishment and maintenance of proliferation arrest in nevi. The authors compared the transcriptomes of melanocytes from healthy human skin, nevi, and melanomas arising from nevi and identified a set of microRNAs as highly expressed nevus-enriched transcripts. Two of these microRNAs—MIR211-5p and MIR328-3p—induced mitotic failure, genome duplication, and proliferation arrest in human melanocytes through convergent targeting of AURKB. Results demonstrate that BRAFV600E induces a similar proliferation arrest in primary human melanocytes that is both reversible and conditional. Specifically, BRAFV600E expression stimulates either arrest or proliferation depending on the differentiation state of the melanocyte. Authors report genome duplication in human melanocytic nevi, reciprocal expression of AURKB and microRNAs in nevi and melanomas, and rescue of arrested human nevus cells with AURKB expression. HoloMonitor M4 is used for cell proliferation, dry cell mass, and death studies.