Customer Publication
Dual-functional injectable hydrogels as antimicrobial and angiogenic therapeutics for dental pulp regeneration†
Journal: Journal of Materials Chemistry B (2025)
Institution: Biomaterials and Nanotechnology Research Group, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Research Areas: Material chemistry
Cell Lines: SVEC4-10 (mouse endothelial cells)
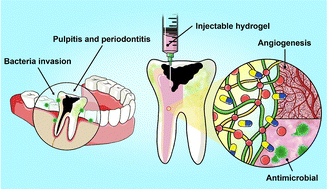
Summary: this study investigates an injectable hydrogel system composed of hyaluronic acid (HA) and carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCs), chemically crosslinked with 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE). The hydrogel demonstrated excellent injectability, self-healing ability, and mechanical stability. In vitro and in vivo assessments confirmed its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and capability for controlled release of therapeutic agents. Notably, the amoxicillin-loaded hydrogel (HACM/AX) showed significant antibacterial properties; while the erythropoietin-loaded hydrogel (HACM/EPO) significantly enhanced endothelial cell proliferation and migration, facilitating angiogenesis for tissue regeneration. These findings highlight the potential of the HACM hydrogel as a dual-function biomaterial with antimicrobial and pro-angiogenic properties, offering a promising alternative for pulpitis treatment and dental tissue engineering. HoloMonitor m4 was used to study the morphological features such as convexity, eccentricity, and cell area, cell proliferation and wound healing.