Customer Publication
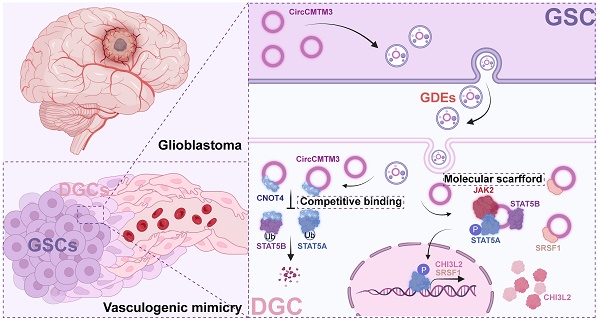
Dual role of exosomal circCMTM3 derived from GSCs in impeding degradation and promoting phosphorylation of STAT5A to facilitate vasculogenic mimicry formation in glioblastoma
Journal: Theranostics (2024)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: GSC01, GSC03 (patient-derived glioblastoma stem cells)
Summary: This paper explores the role of circular RNA (circRNA) in glioblastoma neovascularization. The researchers identified a circRNA, circCMTM3, in exosomes derived from glioblastoma cells, which, when internalized by differentiated glioblastoma cells (DGCs), induces a vascular-like phenotype. circCMTM3 prevents the degradation and promotes the activation of STAT5A, a protein that subsequently increases the expression of genes promoting blood vessel formation. The authors used the single-cell tracking capabilities of HoloMonitor M4 to visualize the migration of DGCs treated with glioblastoma-derived exosomes. They suggest circCMTM3 as a potential target for anti-vasculogenic therapies for glioblastoma.