Customer Publication
Mast Cell Tryptase Promotes Airway Remodeling by Inducing Anti-Apoptotic and Cell Growth Properties in Human Alveolar and Bronchial Epithelial Cells
Journal: Cells (2023)
Research Areas: Cell Biology
Cell Lines: BECs, BEAS-2B, AECs, A549 (Human bronchial epithelial cells, human alveolar epithelial cells,)
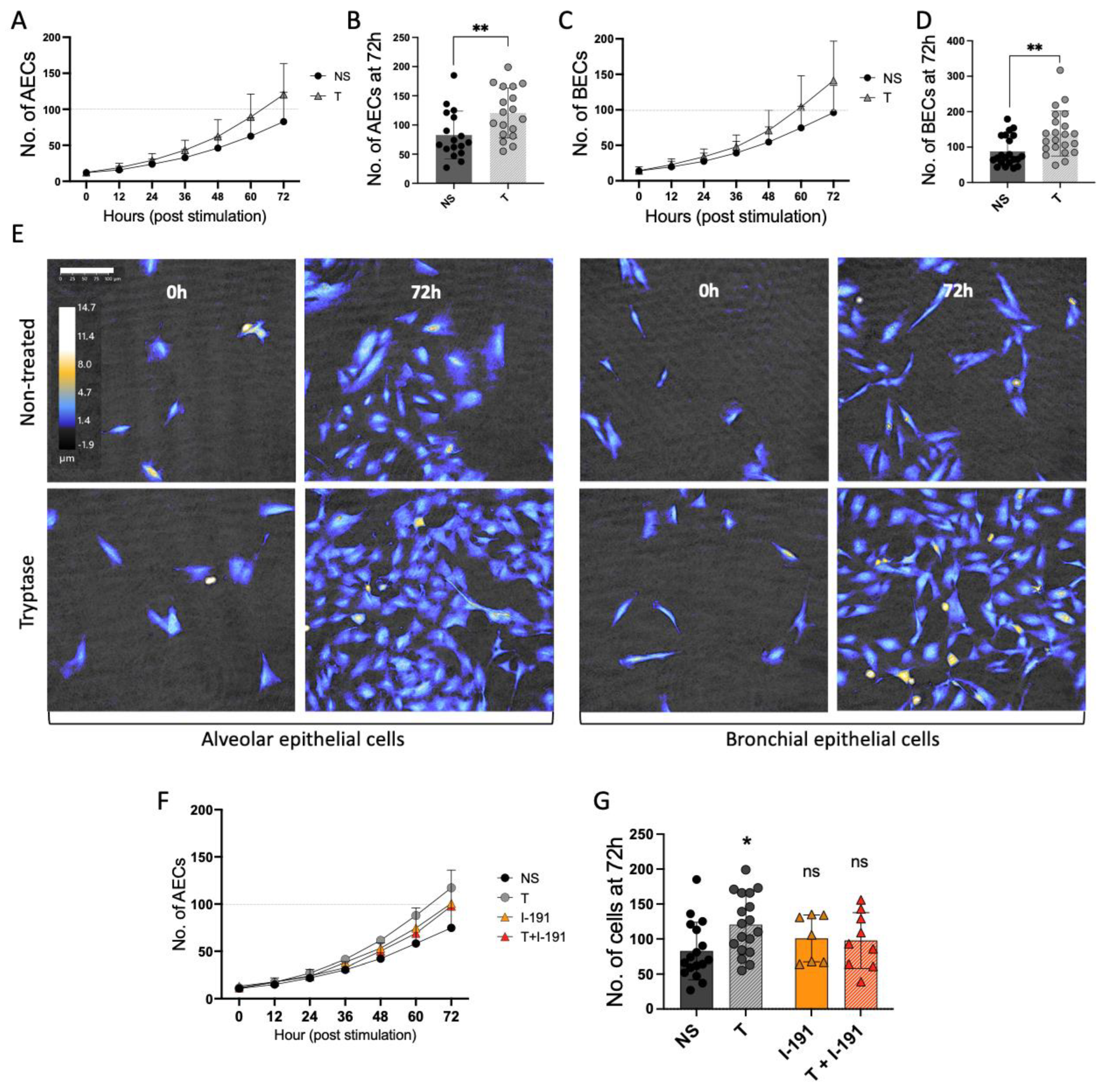
Summary: The article investigates the role of mast cell tryptase in bronchial and alveolar remodeling and the mechanisms of regulation during inflammation. The study found that mast cell tryptase enhanced human bronchial and alveolar epithelial cell growth and shortened the cell division intervals. The elevated cell growth induced by tryptase remained in a pro-inflammatory state. Tryptase also increased the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein BIRC3, as well as growth factor release in epithelial cells1. HoloMonitor is used to investigate the cell growth and cell division effects of mast cell tryptase on bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells.