Customer Publication
The mechanism of BUD13 m6A methylation mediated MBNL1-phosphorylation by CDK12 regulating the vasculogenic mimicry in glioblastoma cells
Journal: Cell Death & Disease (2022)
Institution: Department of Neurobiology, School of Life Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Research Areas: Cancer research
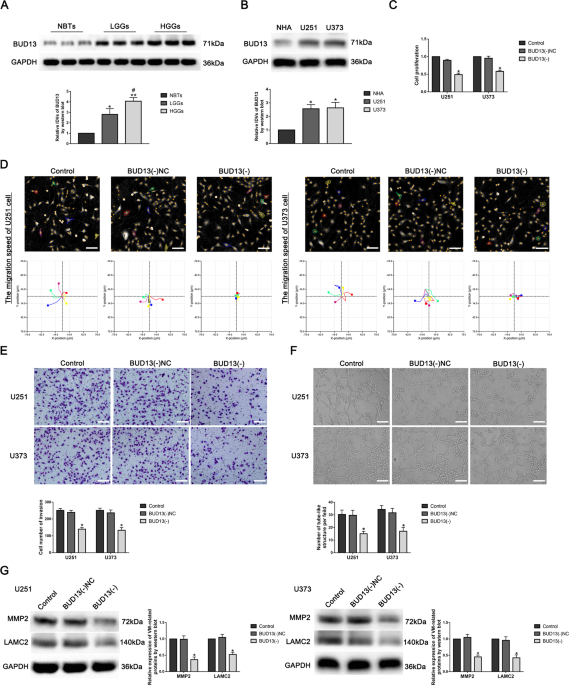
Cell Lines: U251, U373, 293T (Human GBM cell lines, human embryonic kidney)
Summary: Vasculogenic mimicry (VM) is an endothelium-independent tumor microcirculation that provides adequate blood supply for tumor growth. The presence of VM greatly hinders the treatment of glioblastoma (GBM) with anti-angiogenic drugs. Therefore, targeting VM formation may be a feasible therapeutic strategy for GBM. The research aimed to evaluate the roles of BUD13, CDK12, MBNL1 in regulating VM formation of GBM. Knockdown of BUD13, CDK12, and overexpression of MBNL1 significantly inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion, and tube formation of GBM cells. METTL3 enhanced the stability of BUD13 mRNA and upregulated its expression through m6A methylation. CDK12 phosphorylated MBNL1, thereby regulating the proliferation, migration, invasion, and tube formation of GBM. Thus, the BUD13/CDK12/MBNL1 axis plays a crucial role in regulating VM formation of GBM and provides a potential target for GBM therapy. HoloMonitor M4 was used to study the capacity of migration in GBM cells with single cell tracking assay.