HoloMonitor publication highlights 2024
2024 has been an exciting year for us at Phase Holographic Imaging, and we’re thrilled to share some big news: HoloMonitor, our label-free live cell analysis tool, has now been featured in over 300 publications worldwide.
From cancer research to regenerative medicine, HoloMonitor has been helping scientists uncover new insights, without the hassle of labels or damaging cells. That’s right; real-time, high-precision cell analysis, hassle-free.
In this blog, we present the researchers behind these studies and delve into the HoloMonitor publication highlights for 2024, which unlock the secrets of our cells…
Why are researchers choosing HoloMonitor?
The numbers speak for themselves. With 300+ publications from all over the world, proving that HoloMonitor is making an impact on a global scale and becoming a go-to tool for:
- Cancer Research – Tracking how tumor cells react to treatments in real time.
- Drug Discovery – Testing new compounds without altering cell behavior.
- Stem Cell & Regenerative Medicine – Watching stem cells transform into specialized cells.
- Neuroscience & Immunology – Studying neuron interactions and immune responses.
Have you followed our #mondayreads on LinkedIn?
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy (2024)
Spinosyn A exerts anti-tumorigenic effects on progesterone-sensitive ERα-positive breast cancer cells by modulating multiple signaling pathways
Kaniski et. al., University of Michigan-Dearborn, USA
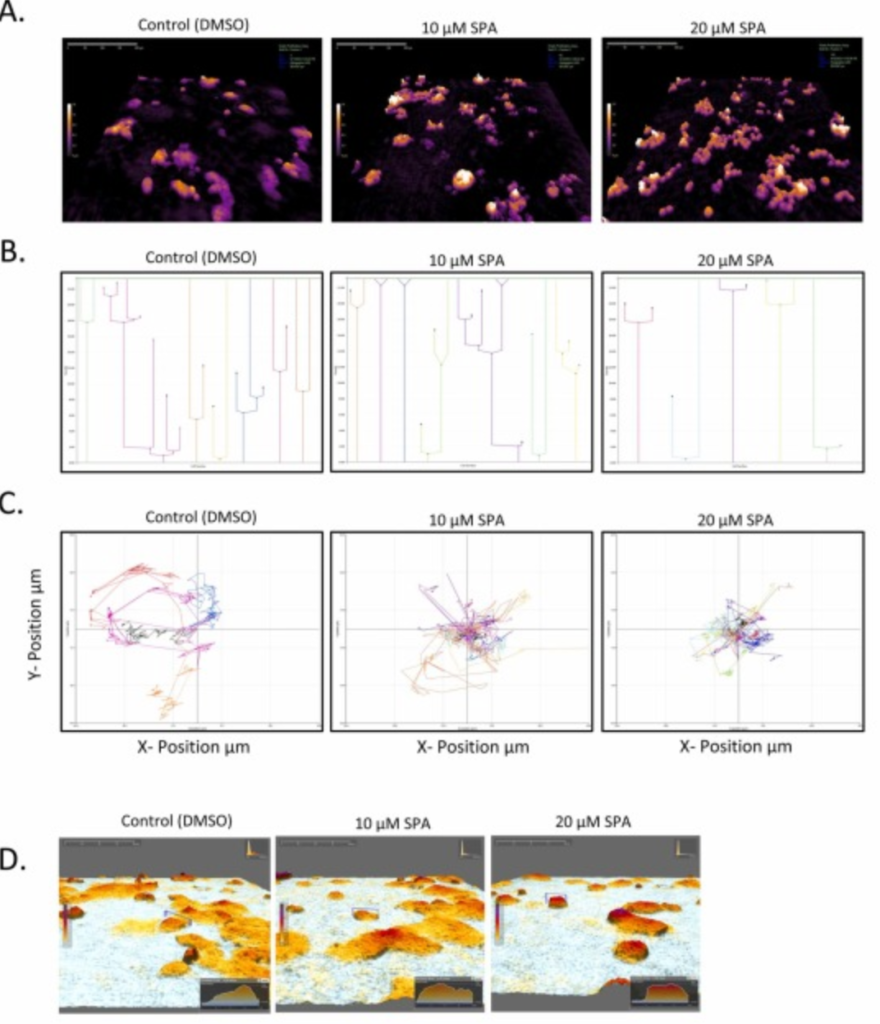
The paper describes the effects of Spinosyn A, a natural insecticide, on breast cancer cells. The authors used HoloMonitor M4 to monitor the effects of Spinosyn A (SPA) on breast cancer cells with cell morphology, proliferation and motility.
The results revealed that the cells are increasing in volume in a concentration-dependent manner when treated with SPA. Single-cell tracking of cell families showed that the cells exhibited longer division times, and their motility was reduced when exposed to SPA. Further morphological analysis reveals that SPA treatment increased shape roughness due to SPA exposure, which is associated with increased apoptosis. On the other hand, irregularity and eccentricity are both decreasing in a concentration-dependent manner. Since cancer cells are highly irregular, a decrease in irregularity suggests that T47-D cells become less cancerous when treated with SPA for 24 hours.
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology (2024)
Quantitative label-free digital holographic imaging of cardiomyocyte optical volume, nucleation, and cell division
Herman Huang et al., San Jose State University, USA
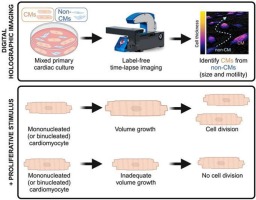
The article investigates how increased cell size and nucleation influence the outcomes of cardiomyocyte cell division in vitro.
In this study, the authors use HoloMonitor M4 to evaluate the proliferative response of mononucleated and binucleated cardiomyocytes to a proliferative stimulus. By tracking long-term cultures at a single-cell level, they monitor cardiomyocyte dynamics in real-time. The findings demonstrate that proliferative stimulus promotes complete cell division in both mono- and binucleated cells, and reveal a link between cardiomyocyte size, nucleation, and cell cycle control. These insights give a better understanding of the cellular mechanisms underlying the loss of cardiac regenerative capacity.
Example outcomes observed in binucleated rat cardiomyocytes stimulated with 5 μM CHIR99021 for 48 h. Time-lapse videos of representative binucleated cardiomyocytes that complete (left), fail to complete (middle), or do not attempt cell division within 48 h (right).
Advanced Biology (2024)
Morphological and Optical Profiling of Melanocytes and SK-MEL-28 Melanoma Cells Via Digital Holographic Microscopy and Quantitative Phase Imaging
Ayah A Farhat et al., University of Michigan-Dearborn, USA
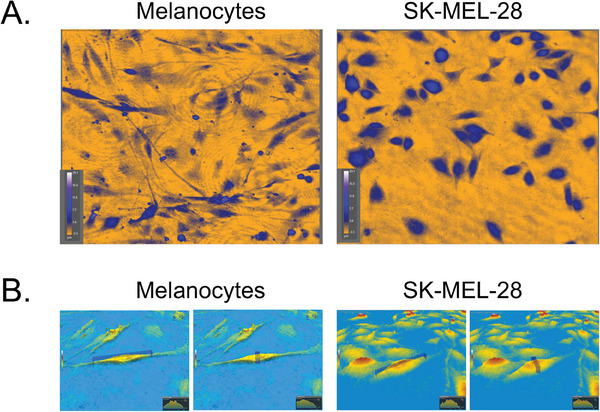
In this study, the researchers utilize digital holographic microscopy and quantitative phase imaging to uncover morphological, optical, and behavioral distinctions between melanocytes and SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells, without the need for labels or any other damaging interventions.
Advanced techniques, including PCA and t-SNE, reveal significant differences in size, shape, optical properties, and migration patterns. These insights support the identification of melanoma biomarkers, enhancing diagnostic precision and therapeutic strategies in melanoma research. HoloMonitor M4 was used to study the morphology and movement between melanocytes and SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells.
We at PHI are especially thrilled that this publication was featured on the cover of Advanced Biology, showcasing images of melanocytes and melanoma cells captured with the HoloMonitor M4. Well done, Farhat and colleagues!
What’s Next?
With this kind of momentum, we’re even more excited to see what 2025 brings. New applications? Breakthrough discoveries? We can’t wait to find out—and to continue supporting the brilliant researchers who are pushing science forward with HoloMonitor.
A huge thank you to all the scientists who’ve trusted our technology. Here’s to another year of innovation!
(P.S. If your lab is one of the 300+, give us a shout—we’d love to hear about your work!)
New HoloMonitor Publications 2024

Exploring the role of PRDX4 in the development of uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma
Journal: Medical Oncology (2024)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: KLE and Ishikawa
Discovery and Characterization of Ephrin B2 and EphB4 Dysregulation and Novel Mutations in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations: In Vitro and Patient-Derived Evidence of Ephrin-Mediated Endothelial Cell Pathophysiology
Journal: Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
Research Areas: Neurobiology
Cell Lines: HBMVECs, HUVECS, HEK293T, CCMECs

Epidermal growth factor potentiates EGFR(Y992/1173)-mediated therapeutic response of triple negative breast cancer cells to cold atmospheric plasma-activated medium
Journal: Redox Biology (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: HEK-293T, SUM-159PT, MCF-7, MDA-MB-468, HCC70, MDA-MB-231 and T-47D
m5C modification of LINC00324 promotes angiogenesis in glioma through CBX3/VEGFR2 pathway
Journal: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: GECs, hCMEC/D3, SVG p12, U-251MG

CDK4/6 inhibitor-mediated cell overgrowth triggers osmotic and replication stress to promote senescence
Journal: Molecular cell (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: hTERT-RPE1 mRuby-PCNA, hTERT-RPE1-FUCCI, MCF7

Oncogenic signals prime cancer cells for toxic cell overgrowth during a G1 cell cycle arrest
Journal: Molecular cell (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: RPE, MCF7 and T47D

The Hippo pathway drives the cellular response to hydrostatic pressure
Journal: The EMBO Journal (2022)
Research Areas: Cell Biology
Cell Lines: HEK293A, 143B
TAAR1 Functions as a Cancer-Inhibiting Gene in Breast Cancer
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: MB-MDA-231