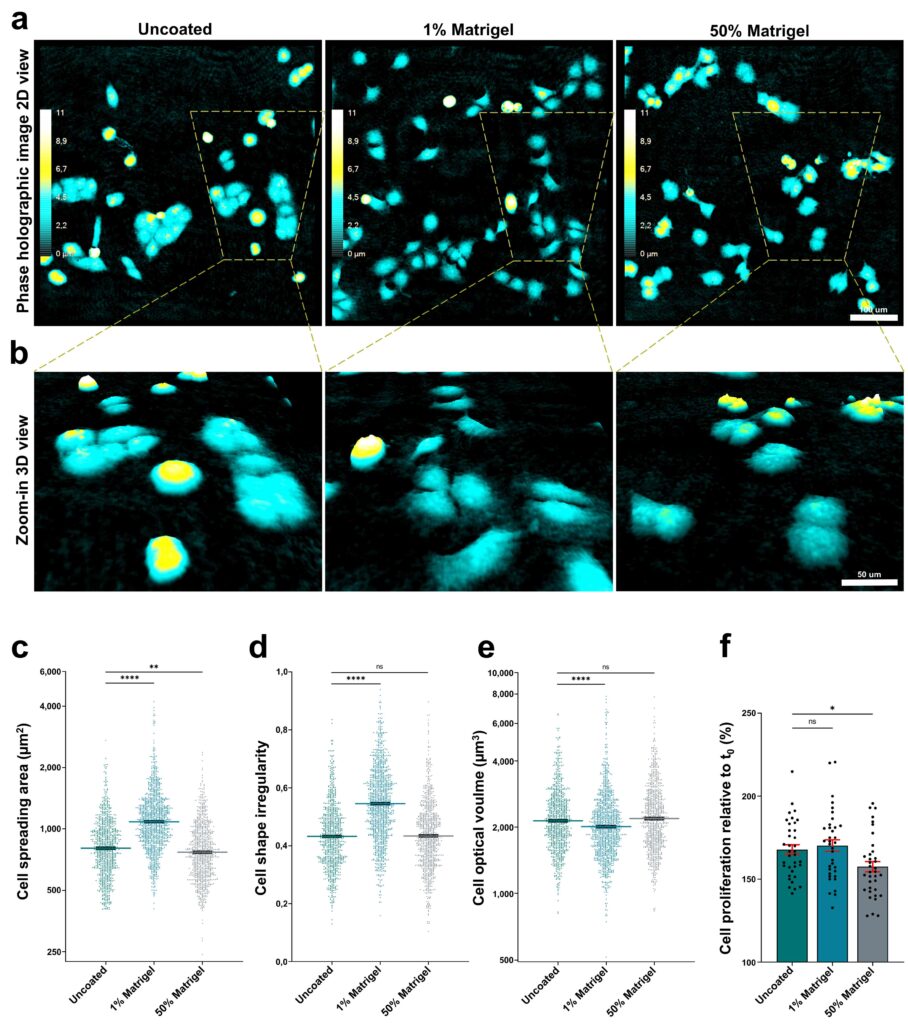
Advancing Cancer Research with Quantitative Live Cell Imaging
Cancer is a leading human disease with persistently high mortality rates. Thus, understanding the how, where, why and with whom metastatic cancer cells disseminate and proliferate is one of the highest importance in cancer research. The HoloMonitor live cell imaging system advances your cancer research with a non-invasive way to measure and quantify cell activity in real-time without compromising the integrity of your precious cells. Therefore, you can get more accurate and native results from your experiments.

A live cell analysis tool with real-time data
Find out more about how HoloMonitor live cell imaging can accelerate your cancer research!
Featured publications within cancer research
Measure mitotic activity in melanocytes
Cutaneous melanoma is deadly skin cancer. The activating mutation BARFV600E mutation exists both in moles and over half cutaneous melanomas.
In this study, in order to investigate why the same mutation has such different consequences in moles and melanomas, the authors using HoloMonitor studied cell proliferation, cell dry mass, cell death and cell growth rate. The experiments showed by increasing the levels of two microRNAs in melanocytes induces mitotic failure, genome duplication, and proliferation arrest. BRAFV600E induces a similar proliferation arrest in primary human melanocytes that is both reversible and conditional depending on the differentiation state of the melanocyte.
On-demand webinar
The secrets to truly controlled cell experiments for cancer research
Find out how HoloMonitor provides better insights by analyzing proliferation, morphology and movement data for both single cells and cell populations.
Discover HoloMonitor Live Cell Assays
Learn more about what you can do with HoloMonitor
Answer cancer research questions with quantitative live cell imaging
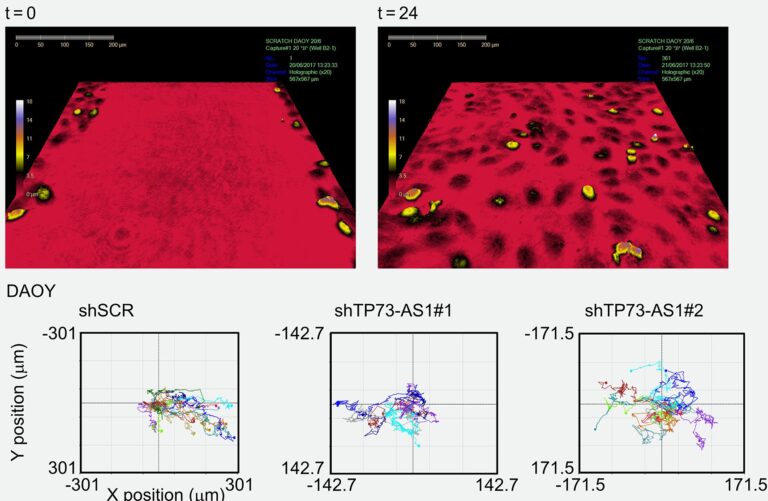
24 hours time-lapse video of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
72 hours time-lapse video of JIMT-1 breast cancer cells
Browsing publications in cancer research
Get inspired by other research fellows, and learn how HoloMonitor quantitative live cell imaging can benefit your cancer research:

Smart drug combinations for cervical cancer: dual targeting of Bcl-2 family of proteins and aurora kinases
Journal: Am J Cancer Res (2020)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: HeLa

SUMOylation of PUM2 promotes the vasculogenic mimicry of glioma cells via regulating CEBPD
Journal: Clinical and Translational Medicine (2020)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: U251, U373
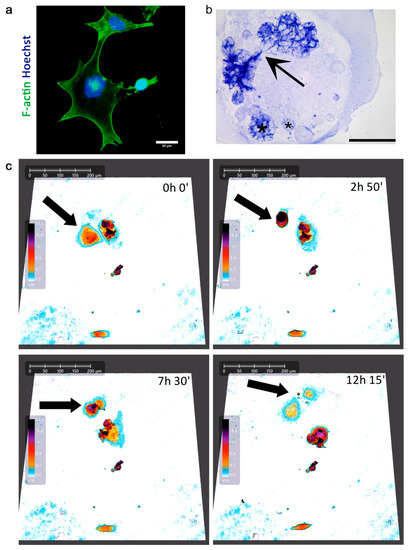
Improved Autophagic Flux in Escapers from Doxorubicin-Induced Senescence/Polyploidy of Breast Cancer Cells
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2020)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: MDA-MD-231
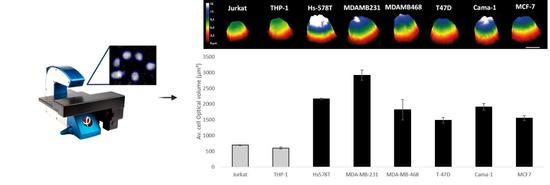
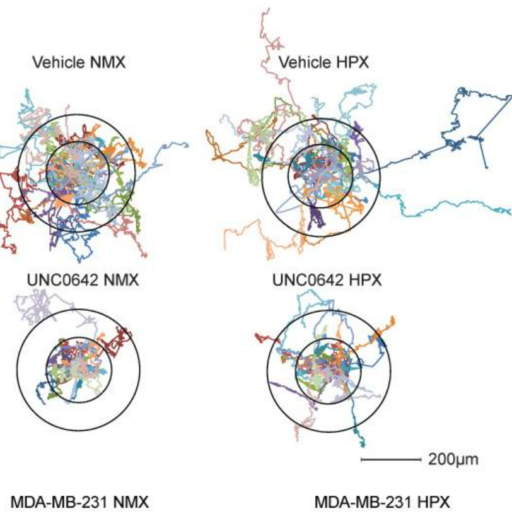
Discrimination between Breast Cancer Cells and White Blood Cells by Non-Invasive Measurements: Implications for a Novel In Vitro-Based Circulating Tumor Cell Model Using Digital Holographic Cytometry
Journal: Applied Sciences (2020)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: Jurkat, THP-1, Hs-578T, MDA-MD-231, MDA-MB-468, T57D, Cama-1, MCF-7
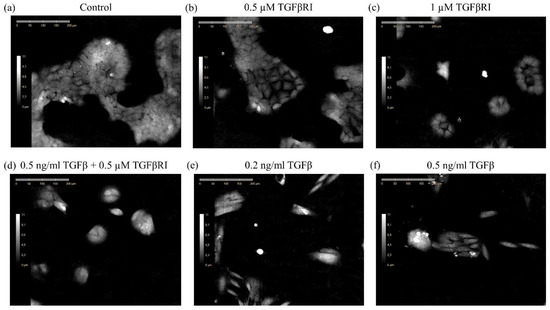
Quantifying the Rate, Degree, and Heterogeneity of Morphological Change during an Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Using Digital Holographic Cytometry
Journal: Applied Sciences (2020)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: HDF, RPTE, L929, NMuMG, JIMT-1
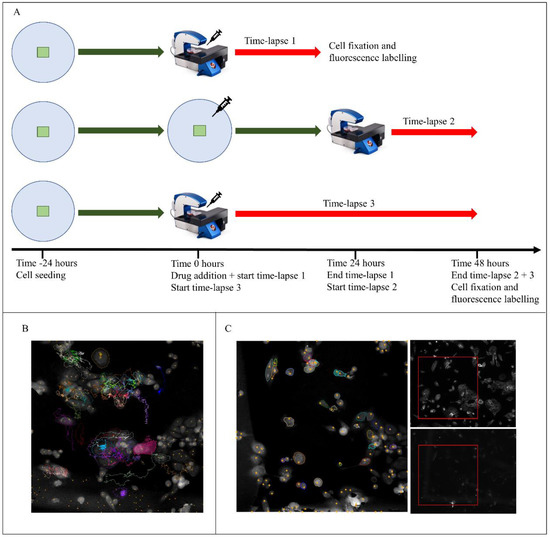
Salinomycin Treatment Specifically Inhibits Cell Proliferation of Cancer Stem Cells Revealed by Longitudinal Single Cell Tracking in Combination with Fluorescence Microscopy
Journal: Applied Sciences (2020)
Research Areas: Cancer research, Stem cell research
Cell Lines: JIMT-1