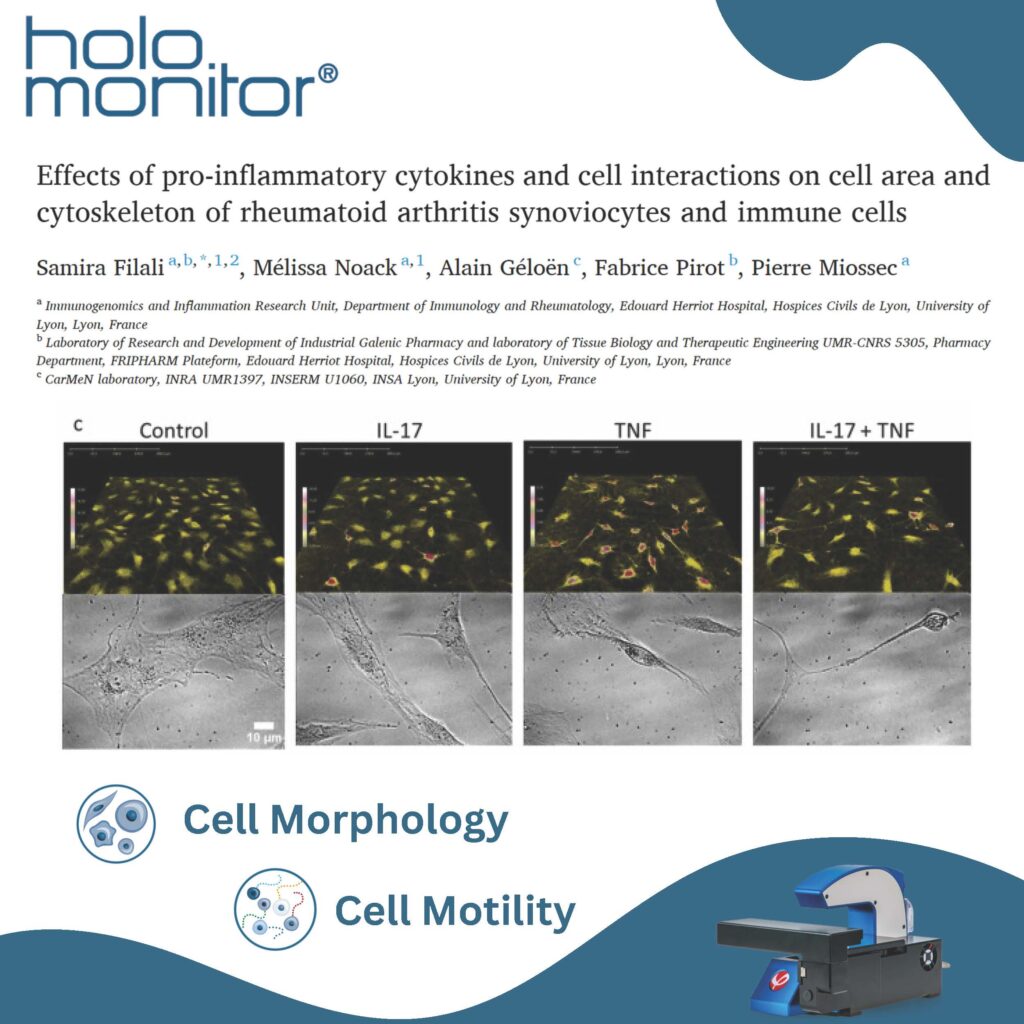
HoloMonitor publication highlights 2023
In 2023, cell researchers all over Europe, the USA, and Asia continued to show the versatility of HoloMonitor in their innovative research. We’re nearing 300 peer-reviewed publications featuring HoloMonitor data — a proud milestone for us at PHI.
This year, HoloMonitor data contributed to diverse fields, from cancer research to immunology. As a helpful tool for studying cell behavior, its label-free Cell Morphology Assay remains a favorite among our users. At the same time, applications like Single-cell tracking and Kinetic cell motility have further gained popularity.
In this blog, we present the researchers behind these studies and delve into the HoloMonitor publication highlights 2023 that unlock our cells’ secrets…
Soon, 300 publications!
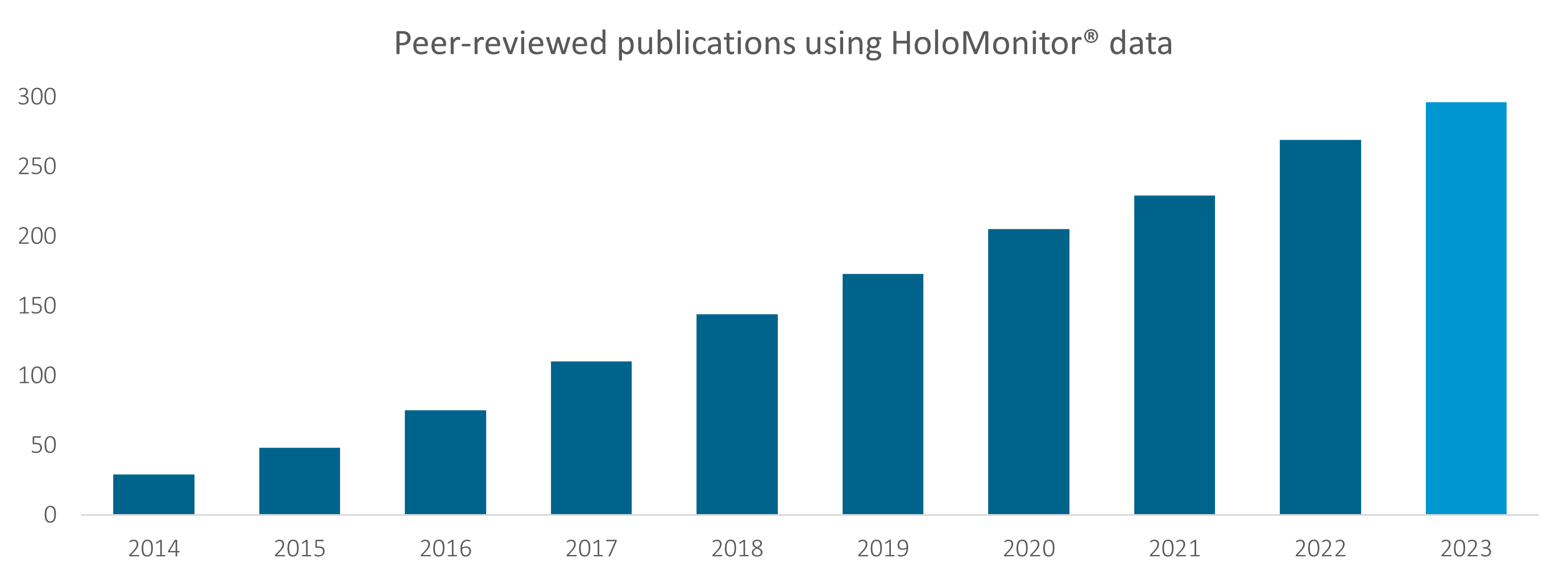
HoloMonitor data has been used in many publications covering various research areas and applications. Browse our publication library to discover more.
Keep on reading!
Below, we highlight a few notable articles from different research fields
that feature HoloMonitor and its range of software assays.
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
IRE1-mediated degradation of pre-miR-301a promotes apoptosis through upregulation of GADD45A
Gebert, Magdalena et al., Medical University of Gdansk, Gdansk, Poland
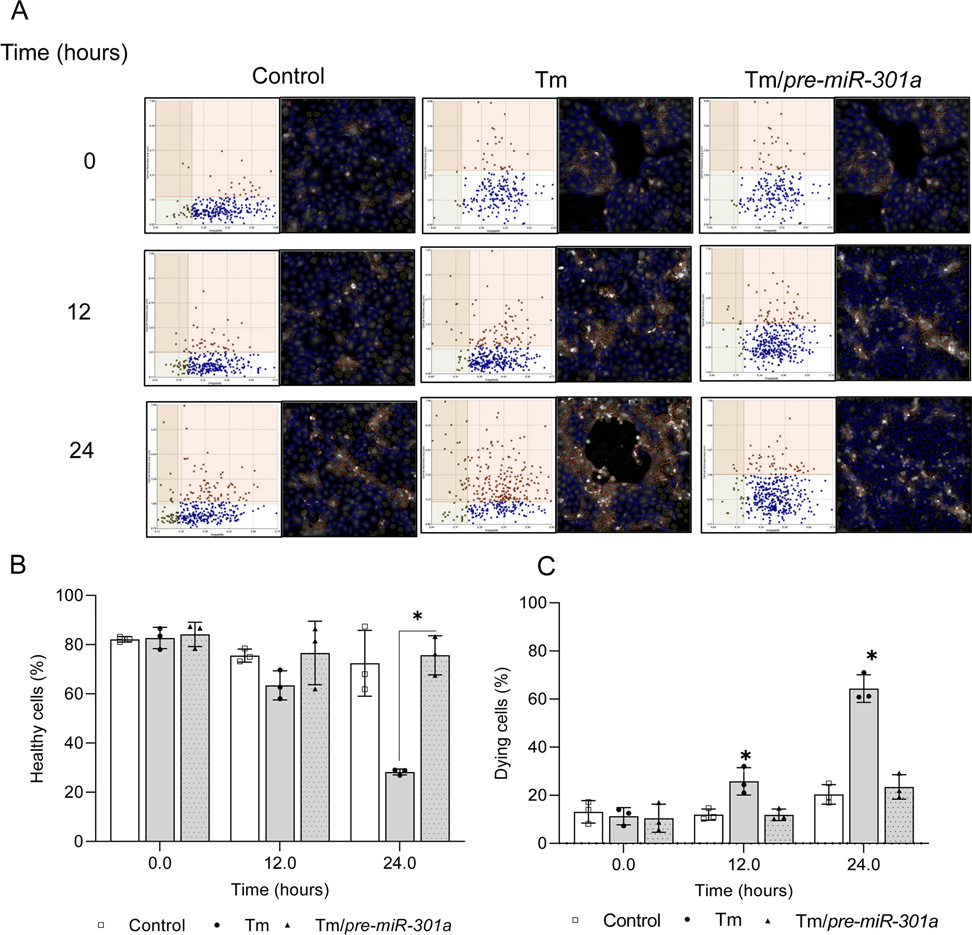
The article investigates the role of IRE1, a key sensor of the unfolded protein response (UPR), in regulating microRNA (miRNA) expression during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress.
The authors use next-generation sequencing (NGS) and nuclear-cytosolic fractionation to show that IRE1 degrades two specific pre-miRNAs, pre-miR-301a and pre-miR-106b, in the nucleus during ER stress. Also, they identify a novel target of miR-301a-3p, a pro-apoptotic UPR factor called GADD45A. They demonstrate that blocking miR-301a-3p binding to GADD45A mRNA increases GADD45A expression and promotes cell death. They conclude that IRE1 has a dual role in the UPR, as it can splice XBP1 mRNA for survival or degrade pre-miR-301a to induce apoptosis.
Gebert et al. use HoloMonitor to measure the cell viability and cell morphology of human bronchial epithelial cells under different conditions of ER stress and miRNA modulation.

The authors use HoloMonitor to measure the cell viability and cell morphology of human bronchial epithelial cells under different conditions of ER stress and miRNA modulation. They show that HoloMonitor can detect changes in cell number, cell area, cell volume, and optical cell thickness in response to ER stress and miRNA manipulation (see Cell Morphology Assay). They also use HoloMonitor to monitor the dynamics of cell death over time and to quantify the percentage of apoptotic cells.
Keywords: cell morphology, microRNA, cell viability, cell biology, protein-ligand interactions, receptors, cytokines, growth factors, Cell Lines: 16HBE14o (human bronchial epithelial)
Have you followed our #mondayreads on LinkedIn?
Communications Biology (2023)
Pseudogene MAPK6P4-encoded functional peptide promotes glioblastoma vasculogenic mimicry development
Zhang, Mengyang et al., China Medical University, Shenyang, China
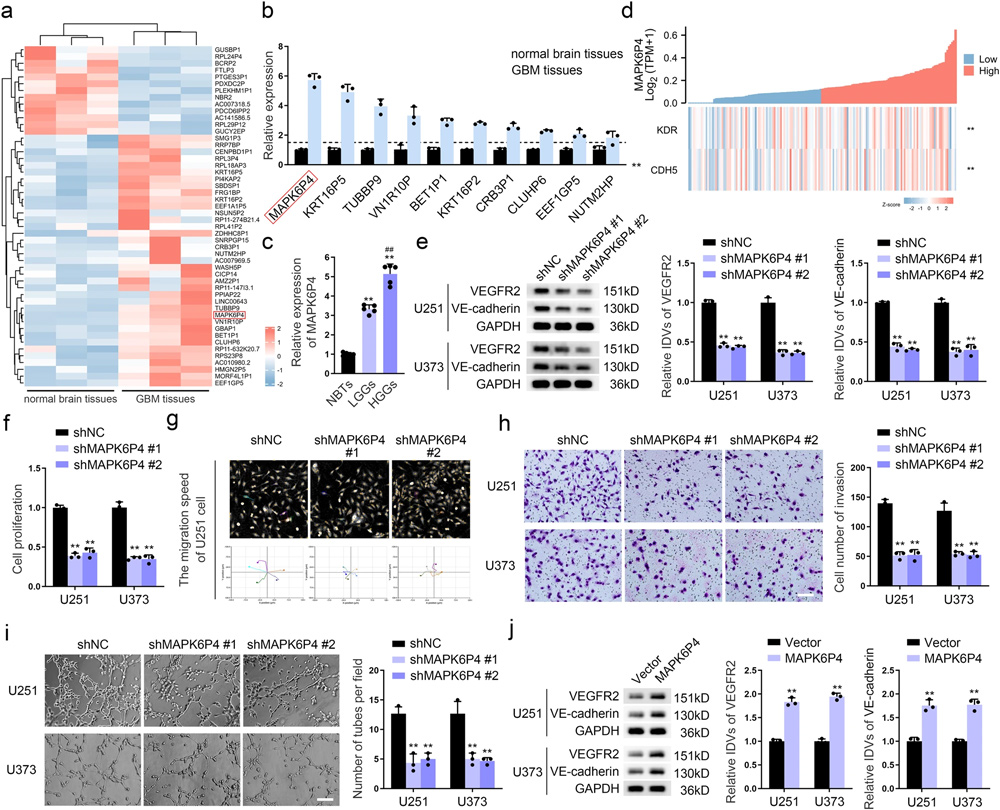
The paper studied the role of a functional peptide encoded by the pseudogene MAPK6P4 in promoting vasculogenic mimicry (VM) in glioblastoma (GBM), a highly aggressive malignant brain tumor.
The study showed pseudogene MAPK6P4 deficiency represses VEGFR2 and VE-cadherin protein expression levels. In addition, it inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion, and VM development of GBM cells. Furthermore, they found that the MAPK6P4-encoded peptide, PEP, is expressed in GBM cells and promotes VM formation by activating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. In addition, the PEP expression is associated with poor prognosis in GBM patients.
Zhang et al. used HoloMonitor to study PEP effects on glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and in vitro vasculogenic mimicry formation ability.

The authors use HoloMonitor (see Single Cell Tracking Assay) to study the effects of PEP on glioblastoma cell proliferation, cell migration, and in vitro vasculogenic mimicry formation ability.
Keywords: glioblastoma, single cell tracking, CNS cancer, phosphorylation, cell migration, vasculogenic mimicry, Cell Lines: U251, U373, HEK 293T cells (human glioblastoma cell lines, human embryonic kidney)
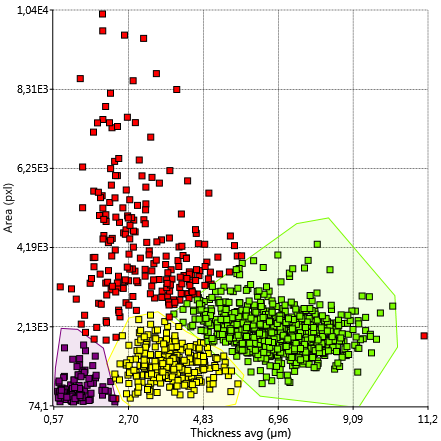
HoloMonitor Cell Morphology
Our users’ most used assay with unique label-free results
We might think of cell morphology as cell area, volume, and maybe shape. However, using HoloMonitor, you can analyze more than 30 different cell morphology features over time. Above all, many of those parameters are unique for label-free QPI imaging. You gain detailed data on every single cell in the population. Furthermore, you can create additional results from the same sample using the other HoloMonitor live cell assays or the add-on fluorescence unit. Learn more in our free cell webinar!
Cells (2023)
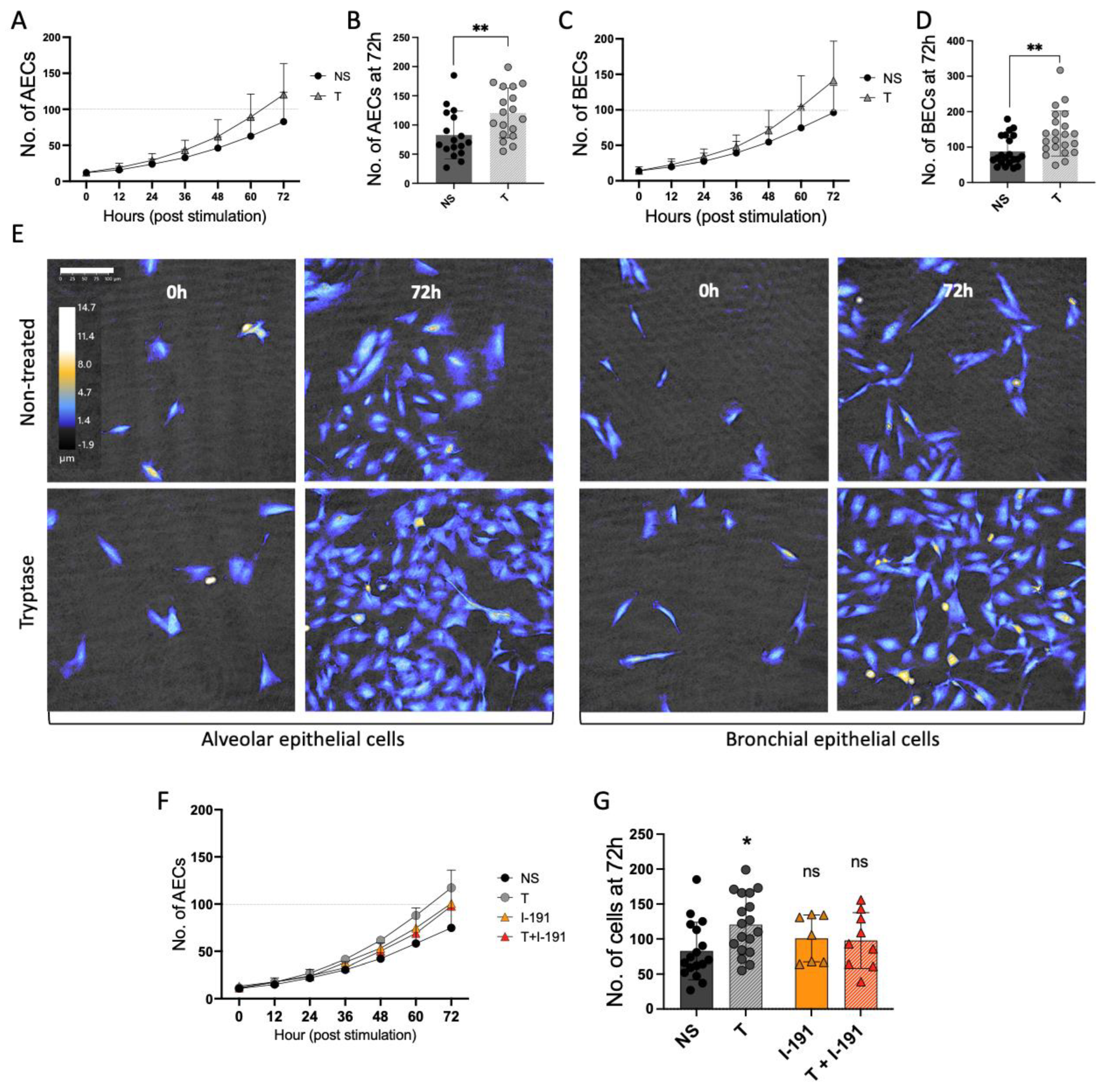
Mast Cell Tryptase Promotes Airway Remodeling by Inducing Anti-Apoptotic and Cell Growth Properties in Human Alveolar and Bronchial Epithelial Cells
Berlin, Frida et al., Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Learn more about Frida’s research in our HoloMonitor user webinar series!
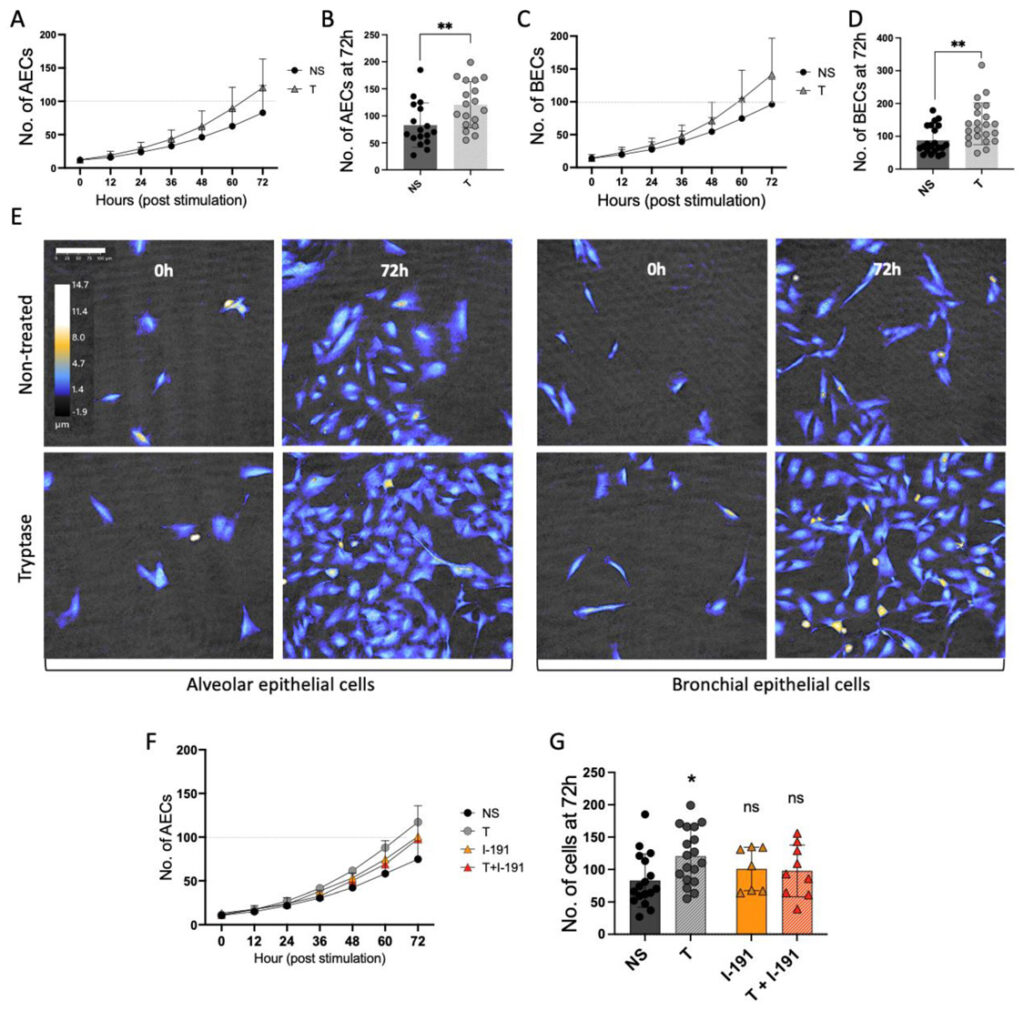
The article investigates the role of mast cell tryptase in bronchial and alveolar remodeling and the mechanisms of regulation during inflammation.
The study found that mast cell tryptase enhanced human bronchial and alveolar epithelial cell growth and shortened the cell division intervals. The elevated cell growth induced by tryptase remained in a pro-inflammatory state. Tryptase also increased the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein BIRC3, as well as growth factor release in epithelial cells.
Berlin et al. used HoloMonitor to investigate the cell growth and cell division effects of mast cell tryptase on bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells.

The authors use HoloMonitor (see Cell Proliferation Assay) to investigate the cell growth and cell division effects of mast cell tryptase on bronchial and alveolar epithelial cells.
The authors performed a thorough and detailed mast cell growth analysis, comparing the cell growth of untreated and tryptase-treated cells. Images were captured every 15 minutes over 72 hours, generating 288 images per focus position and over 2000 images per well and per repeat.
Keywords: cell proliferation, mast cell, proteases, tryptase, bronchial epithelium, alveolar epithelium, growth factors, Cell Lines: BECs, BEAS-2B, AECs, A549 (Human bronchial epithelial cells, human alveolar epithelial cells)
Enriching Publications with Live Cell Videos
HoloMonitor offers high-quality images and videos. Coupled with detailed quantitative data down to a single-cell level, this provides a comprehensive view of cell behavior. This multifaceted data presentation not only enhances the understanding but also strengthens the scientific findings from various perspectives. And it’s beautiful, isn’t it?
Rafnsdóttir et al. (2023), Lund University, Lund, Sweden
There are many amazing HoloMonitor videos featured in this Toxicology Reports publication titled “A New Animal Product Free Defined Medium for 2D and 3D Culturing of Normal and Cancer Cells to Study Cell Proliferation and Migration as Well as Dose Response to Chemical Treatment.”
JIMT-1 cells imaged every 5 minutes for 72 hours
JIMT-1 spheroid cell migration imaged for 72 hours
New HoloMonitor Publications 2023 Overview
Mast Cell Tryptase Promotes Airway Remodeling by Inducing Anti-Apoptotic and Cell Growth Properties in Human Alveolar and Bronchial Epithelial Cells
Journal: Cells (2023)
Research Areas: Cell Biology
Cell Lines: BECs, BEAS-2B, AECs, A549

A role for androgen receptor variant 7 in sensitivity to therapy: Involvement of IGFBP-2 and FOXA1
Journal: Translational Oncology (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: LNCaP, 22Rv1, VCaP

Faradaic Fenton Pixel – Reactive Oxygen Species Delivery using Au/Cr Electrochemistry
Journal: ChemBioChem (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: A375
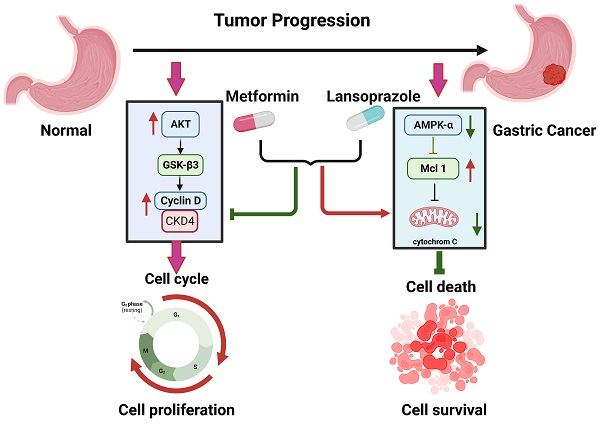
Synergistic Effect of Metformin and Lansoprazole Against Gastric Cancer through Growth Inhibition
Journal: International Journal of Medical Sciences (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: Human gastric cancer cell

SNORD17-mediated KAT6B mRNA 2’-O-methylation regulates vasculogenic mimicry in glioblastoma cells
Journal: Cell Biology and Toxicology (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: U251, U373, human astrocytes, HEK293T

A New Animal Product Free Defined Medium for 2D and 3D Culturing of Normal and Cancer Cells to Study Cell Proliferation and Migration as Well as Dose Response to Chemical Treatment
Journal: Toxicology Reports (2023)
Research Areas: Cell research
Cell Lines: human cancer-associated fibroblasts, keratinocytes, JIMT-1, MDA-MB-231, CaCo-2, MiaPaCa-2, L929
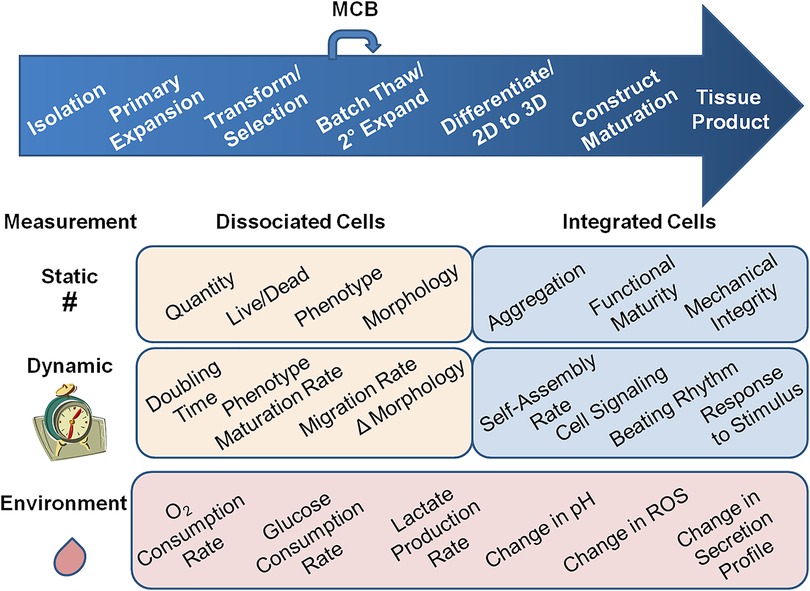
Cytocentric measurement for regenerative medicine
Journal: Frontiers in Medical Technology (2023)
Research Areas: Regenerate Medicine
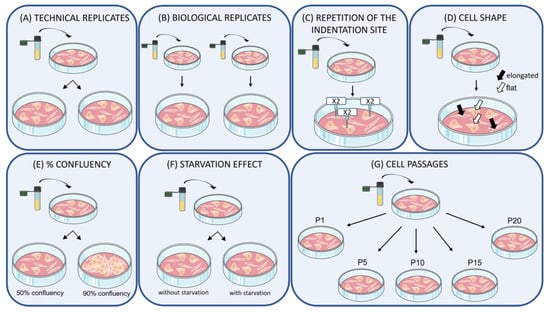
The Impact of Experimental Conditions on Cell Mechanics as Measured with Nanoindentation
Journal: Nanomaterials (2023)
Research Areas: Nanomaterials
Cell Lines: Primary skin fibroblast